How concerned should you be about monkeypox? An expert weighs in
Health officials are investigating the monkeypox outbreak to determine if the virus acquired a mutation that makes it more transmissible or if superspreader events in Europe might be to blame for the current outbreak.
“Anytime the virus does something new, it catches our attention,” said Dr. Richard Kennedy, co-director of Mayo Clinic’s Vaccine Research Group.
Monkeypox is endemic in Central Africa. While outbreaks of monkeypox have occurred before, none has been this large.
“This is a larger outbreak, both in terms of case numbers and the geographic spread. Now we’re trying to figure out if there is something new with the virus. It’s a DNA virus, so it doesn’t mutate as fast as RNA viruses, like influenza and SARS-CoV-2. But DNA viruses do change,” Kennedy said.
Monkeypox is a rare infection that begins with flu-like symptoms followed by a distinctive rash. The rash initially consists of flat patches, then progresses to raised nodules and then to vesicles, with one or two days in each phase. The final stage of pus-filled blisters can last five to seven days.
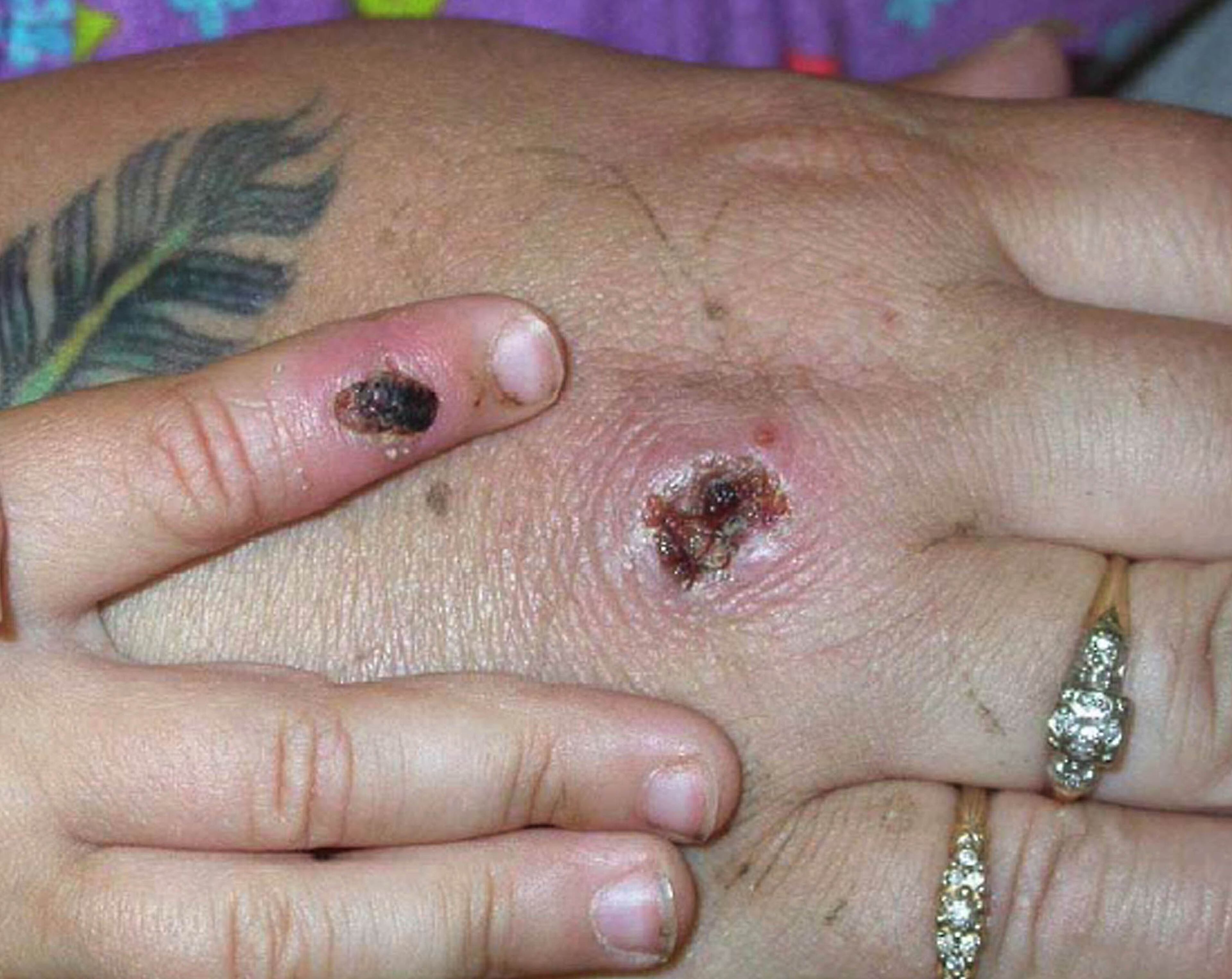
Human-to-human spread of the virus occurs by direct contact with an infected person’s skin or that person’s secretions. Transmission is limited to close household contacts or health care workers not wearing personal protective equipment. People with monkeypox are infectious to others from the onset of fever until all lesions scab over.
While monkeypox can be fatal, the infection will be mild and clear up after a few weeks for most people, Kennedy said. He added the overall risk for the public is low, and it’s not something people should be too concerned about at this time.
“Now that everybody is aware of it, health authorities all over the world are looking for it. So if people develop symptoms, instead of trying to figure out what this is — going through sort of the usual suspects — now we can immediately jump right to let’s check and see if this is monkeypox and isolate these people, and then trying to identify people they’ve come into contact with,” he said.
Vaccines can prevent infection, and treatments are available for those who are exposed or become infected.
“The smallpox vaccine does provide protection against monkeypox. So there are countermeasures available,” Kennedy added. “There’s a vaccine available. It’s not going to be widely available because there are contraindications for it. And a lot of people — at least a third of the U.S. — either has a contraindication or lives with someone who has a contraindication. So you’re not going to see widespread — everybody get vaccinated. There’s no need.”
Smallpox vaccines effectively prevent monkeypox if given before or within a few days of infection.
For more content like this, sign up for the Pulse newsletter here.

